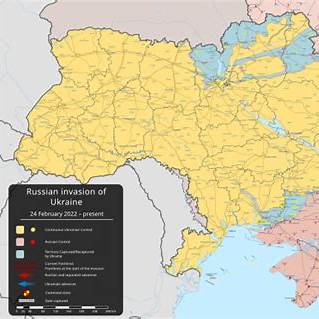
The Russian invasion of Ukraine, initiated on February 24, 2022, marks one of the most significant geopolitical events in recent history. It has caused widespread devastation, human suffering, and global consequences, becoming a critical focal point of international attention.
Background and Prelude to the Invasion
https://www.profitablecpmrate.com/pu1ngaj6i?key=68f7ac79c288a00ee3567f43ae4098ecThe roots of the conflict date back to 2014, when Russia annexed Crimea following Ukraine’s Euromaidan protests. This move triggered international condemnation and sanctions. During the same period, pro-Russian separatists in Ukraine’s Donetsk and Luhansk regions declared independence, leading to armed conflict in the Donbas area. Despite multiple ceasefires and international agreements, tensions remained high.
In late 2021, Russia began amassing military forces near Ukraine’s borders, conducting large-scale exercises that heightened fears of an invasion. In February 2022, Russia officially recognized the self-proclaimed Donetsk and Luhansk republics as independent states. Days later, Russian forces launched a full-scale invasion under the pretext of a “special military operation.”
The Invasion Unfolds
The invasion began with missile strikes targeting Ukraine’s military infrastructure and key cities. Ground forces entered from multiple directions, including Belarus, eastern Ukraine, and Crimea. Initial rapid territorial advances faced strong Ukrainian resistance, causing logistical and operational challenges for Russian forces.
Russian troops reached the outskirts of Kyiv, but fierce battles in areas like Bucha and Irpin hindered their progress. By April 2022, Russian forces withdrew from northern Ukraine, focusing on the eastern and southern regions.
International Response and Sanctions
The international community strongly condemned Russia’s actions. A range of economic sanctions was imposed, targeting Russia’s energy, finance, and defense sectors. These sanctions aimed to isolate Russia economically and diplomatically.
Countries provided Ukraine with significant humanitarian and military support. Weapons, intelligence, and financial aid were crucial in strengthening Ukraine’s defense. Despite international calls for ceasefires, peace negotiations failed to yield substantial results.
Humanitarian Impact
The invasion caused a severe humanitarian crisis. Millions of Ukrainians were displaced, seeking refuge in neighboring countries or becoming internally displaced. Cities like Mariupol and Kharkiv suffered extensive destruction due to relentless shelling.
Reports of war crimes, including attacks on civilians, forced deportations, and executions, surfaced. These allegations are under investigation by international organizations, though accountability remains a challenge amid ongoing conflict.
Military Developments and Stalemate
By 2023, the conflict had evolved into a war of attrition. Both sides engaged in intense artillery exchanges, with limited territorial changes. Ukrainian forces regained some areas through counteroffensives in Kherson and Kharkiv, but Russian troops fortified their positions in other regions.
In late 2024, Russia announced the annexation of four regions—Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia—further escalating tensions. This move was widely condemned as illegal.
Current Situation and Prospects for Peace
As of 2025, the conflict remains unresolved, with ongoing battles and no clear path to peace. The war has reshaped global geopolitics, leading to NATO’s expansion and shifts in international alliances.
The human toll continues to rise, with countless casualties and widespread displacement. Despite immense challenges, the resilience of Ukrainians and international support remain pivotal.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine underscores the fragility of peace and the devastating consequences of conflict. Achieving resolution requires sustained diplomatic efforts and adherence to international law.

